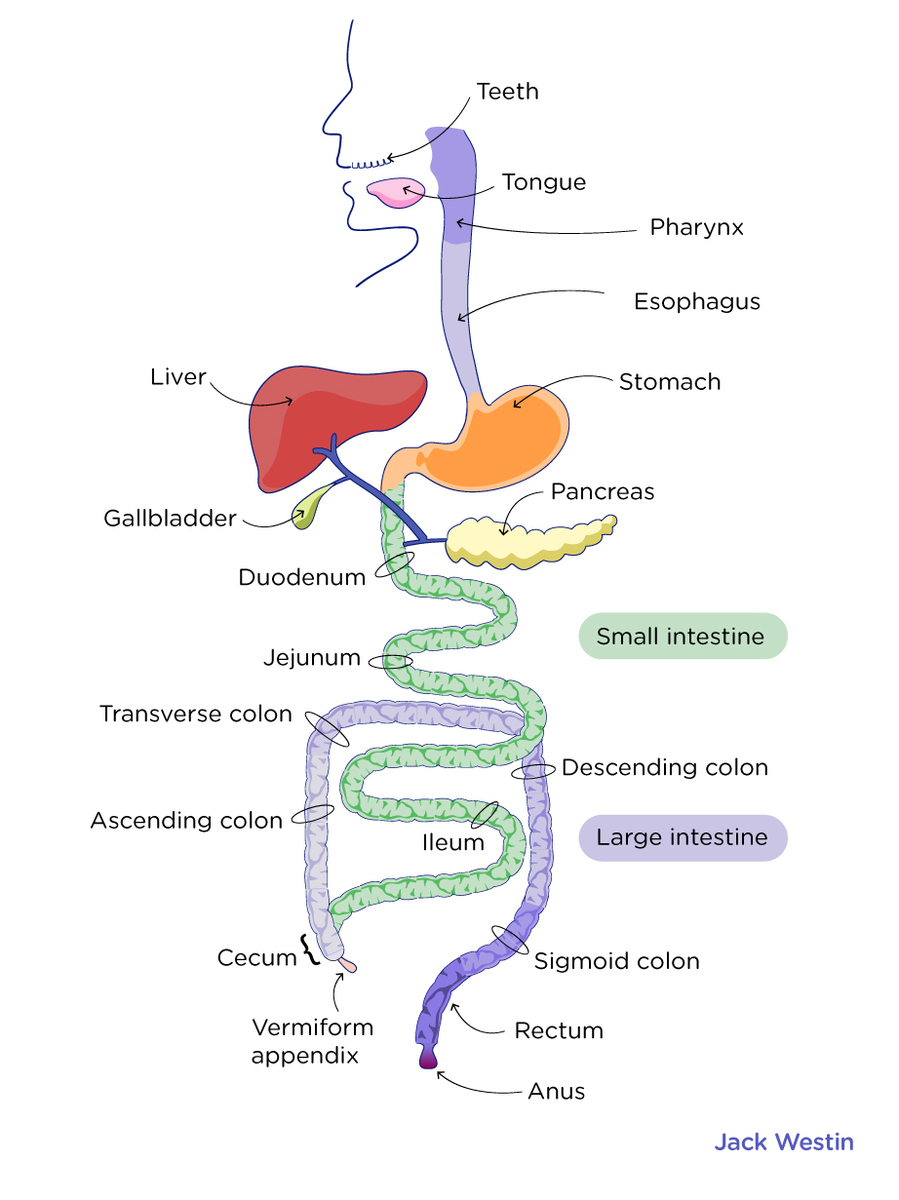
Ingestion is the process by which food is taken into the mouth. The food ingested is chewed by the teeth and formed a mass by mixing with saliva. This is then swallowed and transported via the esophagus to the stomach.
When we eat food it is chewed by the teeth and is mixed with the saliva present in the mouth, this is known as mastication. This forms a mass of food known as a bolus. This is lubricated by saliva and the enzyme mucin present in the saliva. The lubrication helps in an easy swallow of the bolus. The saliva also contains amylase enzyme that starts the digestion of the carbohydrates present in the bolus. The lysozymes present in the saliva provide kill the pathogens present in the bolus.
From the mouth, the food is swallowed via the pharynx into the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube-like muscular organ that transports the bolus to the stomach for further digestion. This occurs with the help of peristalsis in the esophagus that pushes the food towards the stomach.
Key Points
• Ingestion is the process of taking in food into the mouth (oral cavity).
• The food is chewed by the teeth and converted into a bolus with the help of saliva.
• Saliva contains mucin that provides lubrication to the bolus, amylase enzyme that starts the digestion of carbohydrate (starch and glycogen) and lysozyme that kill the pathogen.
• The food is swallowed from the mouth via the pharynx and esophagus into the stomach by peristalsis action of the esophagus. This is known as the transport function.
Key Terms
bolus: a semi-solid mass of food formed due to mastication by the action of teeth, tongue, and saliva.
lysozyme: an enzyme present in the saliva that provides lubrication
saliva: watery fluid secreted from salivary glands in the mouth
peristalsis: contraction in the smooth muscle of the esophagus that helps in the transport of food
mastication: the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth
amylase: a common enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates
esophagus: a tube-like muscular organ that transports the bolus to the stomach for further digestion